FLASH ALERT – Breached Fortinet Config Data Released
On Tuesday, 14 January 2025, a threat group known as “BELSEN GROUP” publicly released 1.4GB of config data for FortiGate, impacting over 15,000 credentials. The data was advertised on Breach Forums, and given away for free via the group’s onion site.
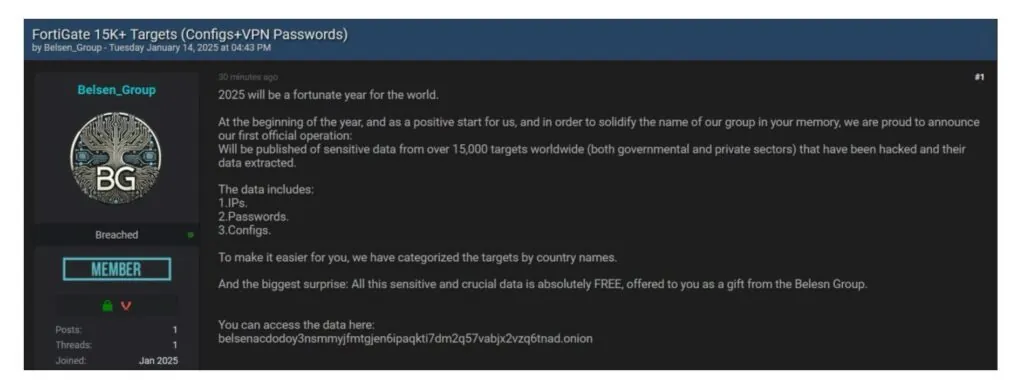
Security researcher Kevin Beaumont reviewed the data and confirmed its authenticity. Given artifacts left over in the data, it is believed this data was breached due to exploiting CVE-2022-40684, a FortiGate firewall vulnerability exposed in October 2022. While a patch has since been released, it is suspected this data was obtained before the vulnerability was patched.
Event Timeline:
- 2022 Incident: Fortinet disclosed CVE-2022-40684, a zero-day vulnerability in Fortigate firewalls actively exploited by attackers. Organisations were urged to patch immediately.
- January 2025: Threat group “BELSEN GROUP” publicly released a dataset containing configurations for over 15,000 Fortigate devices.
Key Details of the Data Dump:
- Contents:
- Usernames and passwords: Some stored in plaintext.
- Device management digital certificates.
- Complete firewall rules.
- VPN user lists.
- Verification: Security researcher Kevin Beaumont confirmed the dump’s authenticity by cross-referencing Shodan data with serial numbers from the release.
- Data Origin: Exploitation of the CVE-2022-40684 vulnerability in 2022. The data was likely stolen in October 2022 but only disclosed publicly in January 2025.
Potential Impacts
- Immediate Risk:
- Organisations exploited in 2022 (even if they patched later) now face exposure of critical data.
- Public availability of device configurations significantly increases the risk of further attacks.
- Exposure Scope:
- Detailed network architectures and user credentials are now accessible to malicious actors.
- Organisations must assess the compromise of VPN and administrative credentials.
Recommendations
- Immediate Actions:
- Verify if your organisation’s IPs are part of the affected list (to be published by researchers).
- Change all device credentials, including admin and VPN users.
- Reassess firewall rules and configurations for potential abuse.
- Long-term Mitigation:
- Confirm patches for CVE-2022-40684 were applied.
- Evaluate additional layers of defence to prevent exploitation of similar vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response:
- Conduct forensic analysis if affected to determine the extent of historical exploitation.
- Engage with security vendors for remediation and further threat intelligence.

