15 – 21 July 2024
CVE Discussion
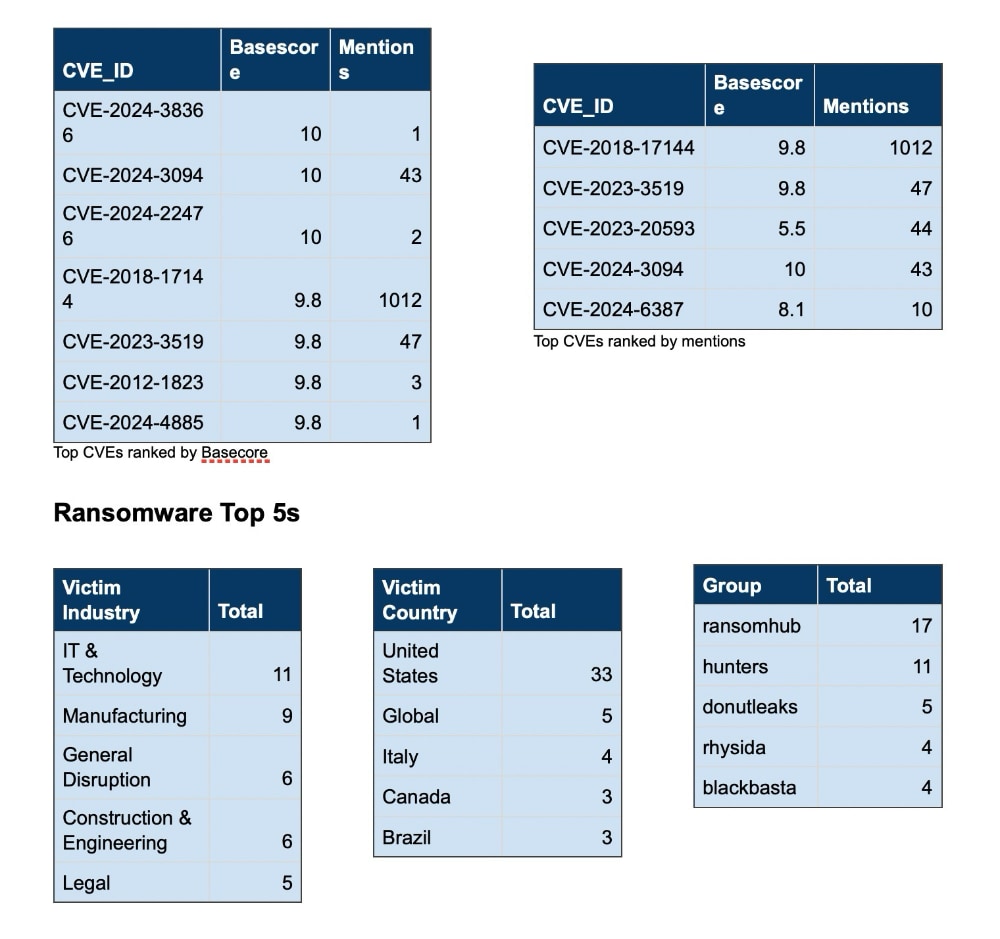
Over the past week, we’ve monitored our vast collection of new data to identify discussions of CVEs.
News Roundup
Ransom paid by AT&T
AT&T recently paid $370,000 to a hacker affiliated with the ShinyHunters group to delete manipulated client data, including call and text metadata, which had been compromised between May 2022 and January 2023. The breach occurred from April 14th to April 25th, 2024, through unauthorised access to AT&T’s third-party cloud platform. The compromised data included phone numbers, communication dates, and call durations, but did not involve the actual content of conversations or text messages.
The payment was made in Bitcoin, and the hacker confirmed the data deletion through a demonstration video. Despite this effort to erase evidence, there is concern that some information might still be accessible, potentially posing ongoing security risks for AT&T’s consumers.
Compromise of Squarespace domain names
Squarespace customer accounts were compromised by hackers, leading to unauthorised access to sensitive information such as email addresses and account details. The breach was attributed to a third-party vendor, highlighting concerns about the security measures in place for customer data. In response, Squarespace has notified affected users and is working to enhance their security protocols.
To protect their accounts, customers are urged to change their passwords and enable two-factor authentication. This incident underscores the persistent risks associated with third-party integrations in the digital environment and the importance of robust security measures.
22 minutes to exploit
Cloudflare’s Q1 2024 Application Security Report reveals that it takes hackers an average of just 22 minutes to exploit newly disclosed vulnerabilities, highlighting a concerning trend in cybersecurity. The report indicates that Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks remain a significant threat, constituting 37.1% of mitigated traffic, while automated traffic makes up one-third of all internet activities, a substantial portion of which is malicious.
Additionally, API traffic has increased to 60%, with many organisations regularly missing a large number of their public-facing API endpoints. The report also underscores the growing use of zero-day exploits and the challenges posed by third-party integrations in web applications, emphasising the constantly evolving cybersecurity threat landscape.
Exploiting the Crowdstrike Issue
On July 19, 2024, Windows systems were impacted by an issue with the CrowdStrike Falcon sensor, which cybersecurity experts have flagged as a serious concern. Hackers exploited this vulnerability to target CrowdStrike customers through phishing campaigns, social engineering, and the distribution of potentially harmful software. The attackers impersonated CrowdStrike support, falsely claiming the issue was a content update error rather than a security problem.
This incident underscores the need for companies to authenticate communication channels and adhere to official guidance on modern threats. Additionally, it highlights the importance of educating employees about behaviours that could compromise security, helping to strengthen defences against such opportunistic attacks.
Photo by Joshua Hoehne on Unsplash

