SOS Intelligence is currently tracking 193 distinct ransomware groups, with data collection covering 384 relays and mirrors.
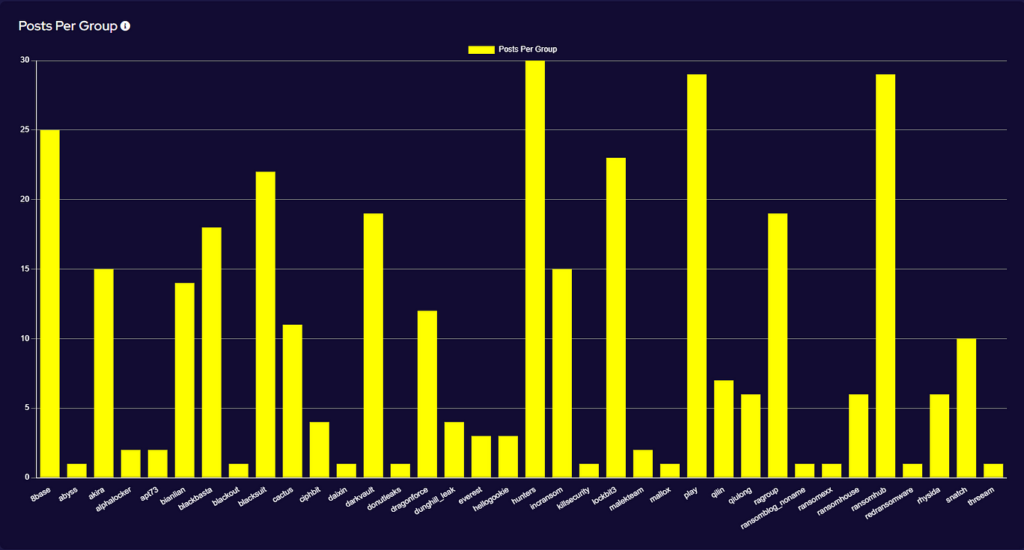
In the reporting period, SOS Intelligence has identified 474 instances of publicised ransomware attacks. These have been identified through the publication of victim details and data on ransomware blog sites accessible via Tor. While this data represents known and publicised data breaches and ransomware attacks, the nature and operation of these groups means that not every successful attack is published and made public, so true figures on the volume of attacks are likely to be higher. Our analysis of available public data is presented below:
Threat Group Activity and Trends
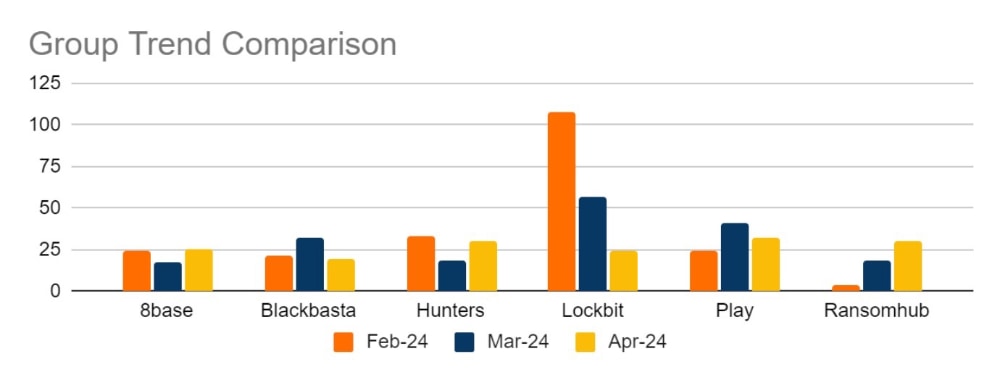
Ransomware activity showed a 30% increase in May when compared to the previous month, and a 4% increase in activity when compared to the previous year. Furthermore, the number of active groups has increased to 37 from 36 the previous month.
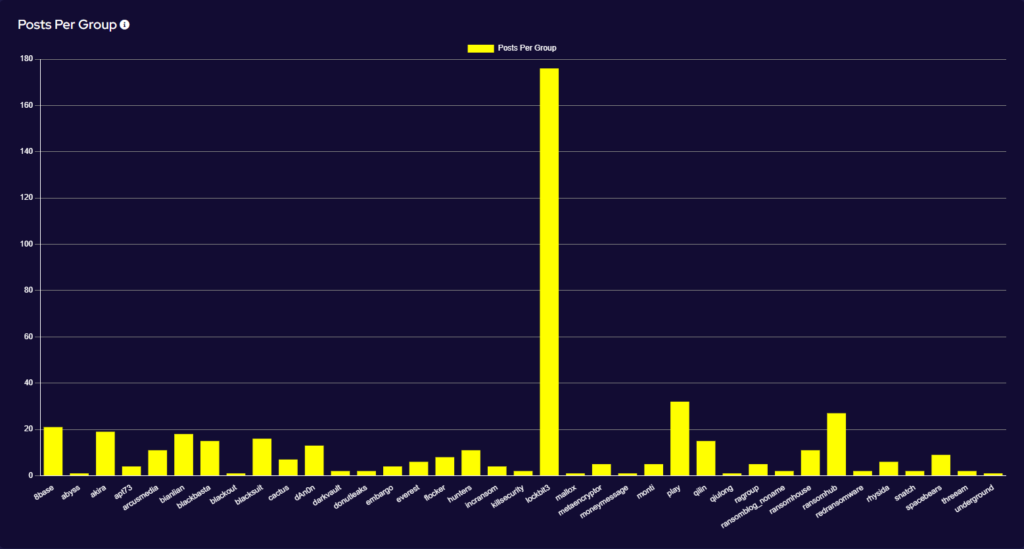
This significant increase in activity has been driven by a surprise surge of activity from the Lockbit group. In May, the group published 176 victims to its Data Leak Site (DLS), representing 37% of all publicised attacks for the month. Further, this is a 633% increase in activity from the previous month and comes at a time when Lockbit was expected to be showing a continued decrease in activity. Rather what we have seen is Lockbit’s busiest month on record.
The sudden surge from Lockbit has been a surprise to many. The first tranche of published data emerged shortly after further law enforcement announcements regarding the group and its takedown. Notable among the data released is an unusually high volume of affected victims in Spain and India being released quickly. This may indicate the activity of an affiliate or affiliates with a particular proclivity for targeting those countries. It should be noted that some of the victims had previously had their data released in the previous year, suggesting that Lockbit might be recycling data for additional ransoms and also to appear active. Furthermore, it isn’t clear when these victims were targeted, so the actual point of breach may have been before law enforcement activity against Lockbit in February 2024.
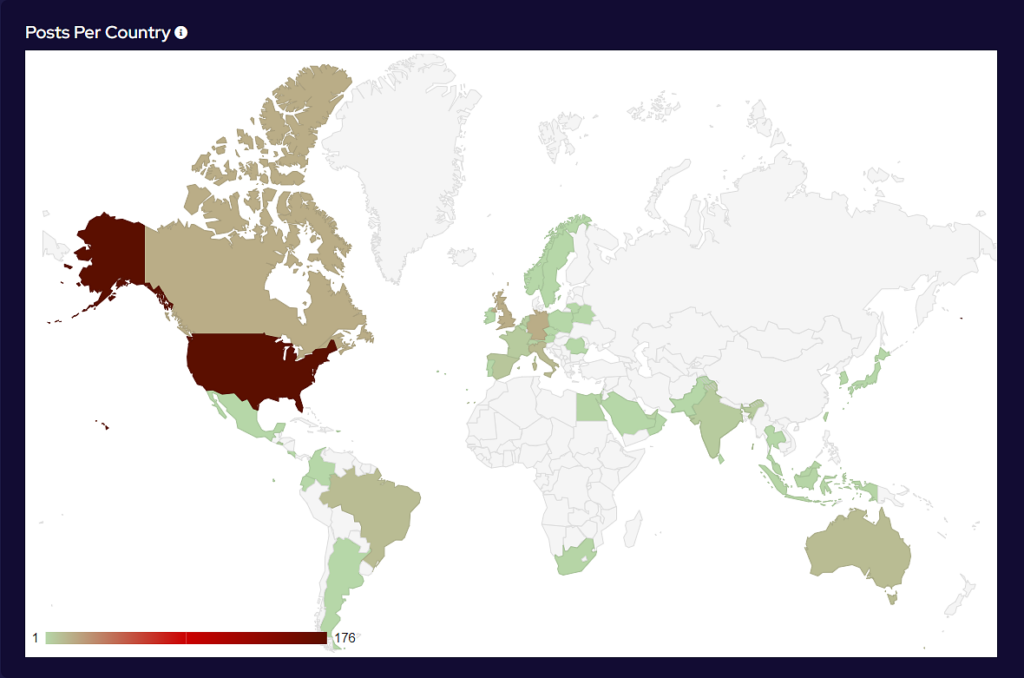
Analysis of Geographic Targeting
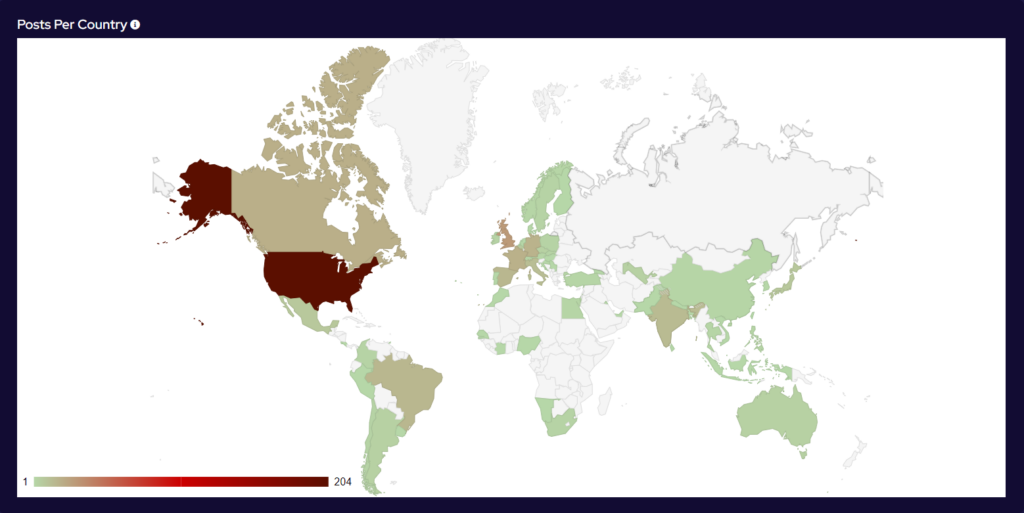
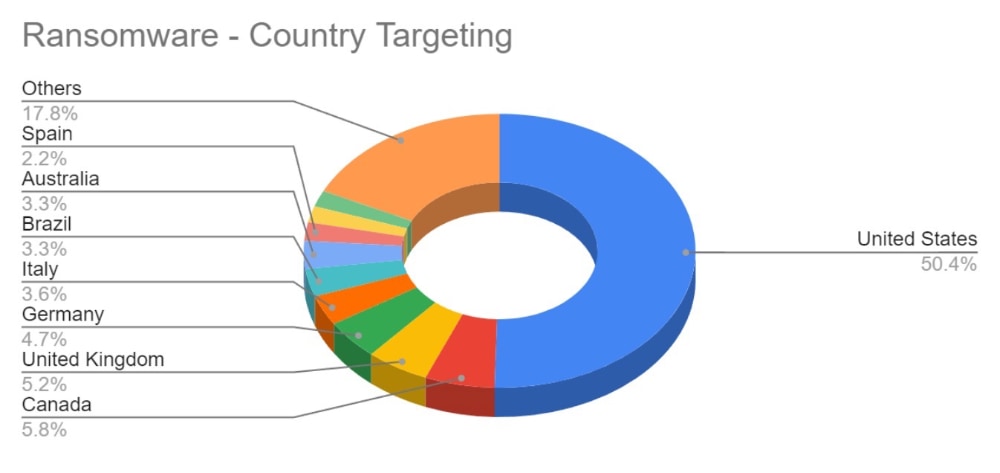
Over the last month, the percentage volume of attacks against the US dropped by 7%. Targeting continues to follow financial lines, with the majority of remaining attacks targeted at G7 and BRICS bloc countries.
Compared to April, 41% more countries were targeted in May. Our data is also showing interesting geographic targeting data. We have observed emerging or developing strains targeting developing countries in Southeast Asia, Africa and South America, whereas more established variants focus more on North America, Western Europe and Australia.
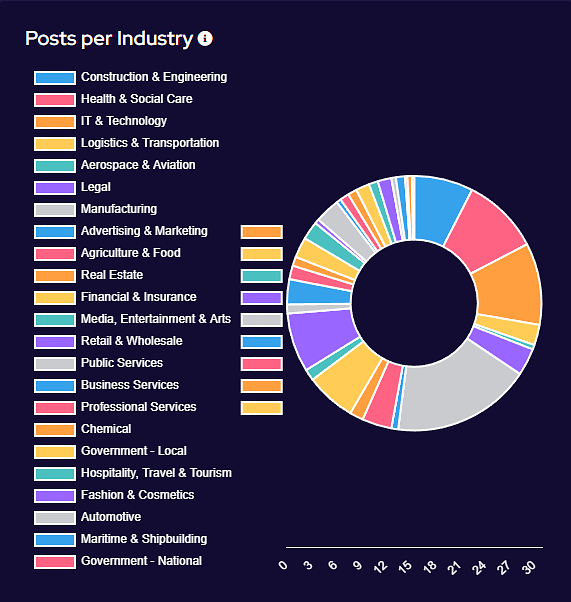
Industry Targeting
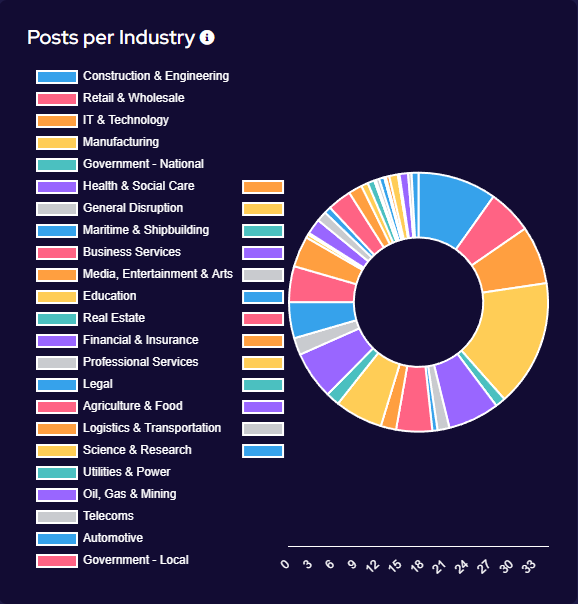
Targeting has broadly increased across all victim sectors, however significant increases have been seen in the Manufacturing, Construction & Engineering and IT & Technology industries.
Notably, there appears to have been increased targeting against public-sector entities. This is likely a result of many groups abandoning their affiliate rules on targeting of such victims.
Significant Events
LockBit Black distributed via Botnet in the wild
Since April, the Phorpiex botnet has sent millions of phishing emails to distribute LockBit Black ransomware. These emails, often sent using aliases with simple names, include ZIP attachments containing executables that install the ransomware. Leveraging LockBit 3.0’s leaked builder, the campaign targets various industries worldwide. Active for over a decade, the Phorpiex botnet has evolved from a worm to an IRC-controlled trojan, and has been implicated in sextortion and cryptocurrency theft.
Social engineering attacks delivering Blackbasta
Researchers have observed the threat actor Storm-1811 using Microsoft Teams and Quick Assist for social engineering attacks that result in the deployment of Blackbasta ransomware. Storm-1811 employs voice phishing (vishing) and malicious links to gain access through Quick Assist. They use tools such as Qakbot, remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools like ScreenConnect and NetSupport Manager, and Cobalt Strike. Additionally, Storm-1811 utilises EvilProxy phishing sites and SystemBC for persistence and command-and-control. After compromising a system, they use PsExec to deploy Black Basta ransomware.
INC Ransomware source code for sale
Threat actor “salfetka” is alleging to have for sale the source code to INC Ransom, valued at $300,000. The legitimacy of the sale is uncertain. This comes at a time where there have been changes within the groups operation, which suggests possible plans for a new encryptor.
Threat actors targeting Windows admins with fake ads
A ransomware campaign is targeting Windows system administrators by promoting fake download sites for Putty and WinSCP through search engine ads. These fraudulent sites offer Trojanized installers that deploy the Sliver toolkit, facilitating further network access and potential ransomware deployment. The campaign employs tactics similar to those used by BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware, highlighting an increasing threat from search engine advertisements for popular software.
New Groups
SpiderX
SpiderX, a new ransomware-as-a-service promoted by threat actors on underground forums, is designed for Windows systems and boasts advanced features surpassing its predecessor, Diablo. Key capabilities include ChaCha20-256 encryption for rapid file encryption, offline functionality for stealth operations, comprehensive targeting of all connected drives, and a built-in information stealer that exfiltrates data to MegaNz. Priced at $150, SpiderX poses a significant cybersecurity threat due to its affordability and efficiency.
Fakepenny
Researchers have identified a new North Korean hacking group, Moonstone Sleet, active since August 2023. This threat actor employs custom ransomware called ‘FakePenny,’ first detected in April 2024, which includes a loader and an encryptor with ransom notes resembling those used by Seashell Blizzard’s NotPetya. Moonstone Sleet’s ransom demands are notably high, with one reaching $6.6 million in Bitcoin, surpassing previous North Korean ransomware demands such as WannaCry 2.0 and H0lyGh0st.
Arcusmedia
First identified in May, the Arcusmedia group has been responsible for at least 17 incidents to date, primarily targeting South America across a wide range of sectors, including government, banking, finance, construction, architecture, music, entertainment, IT, manufacturing, professional services, healthcare, and education.






Recent Comments